You might have heard about GEO — an emerging counterpart to search engine optimization (SEO) that’s gaining momentum in B2B marketing. SEO has been a tried-and-true strategy for boosting brand visibility online, but, in the AI era, Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is quickly becoming a critical element of brand visibility campaigns as well. For decades, Google has served as the primary gateway to the internet. With over 90% market share, it’s the first stop for anyone looking to solve a problem, learn about a topic, or research a company or product.
However, the advent of generative AI has started to shift the landscape. To stay competitive, brands must now optimize their websites not only for search engines but also for AI platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini (owned by Google). That’s where GEO enters the picture — ensuring your brand’s voice is heard and your content is effectively leveraged in this evolving digital ecosystem.
In this article you will learn:
- What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
- Why is GEO Important in 2025 and Beyond?
- How do Generative Engines Work?
- What’s the Difference Between Generative Engine Optimization and SEO?
- 6 Key Ingredients of a Successful GEO Strategy
- Working with Walker Sands to Expand Your Generative Engine Footprint
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing content and website structure for AI-driven generative models to ensure that your brand’s message is accurately represented and effectively distributed.
Unlike traditional SEO, which primarily focuses on authoritative backlink building and optimizing website pages and content for keyword relevance for search engines like Google, GEO is about ensuring that AI systems also understand the broader context of the content, its relation to the brand, and more layers of detail. With GEO, brand citations from relevant sources can substantially boost contextualism.
GEO can involve training AI models on brand-specific data and iterating content based on AI-generated insights. It also entails optimizing foundational technical website elements that allow AI engines to discover, read, and include a brand’s content in generative AI responses. Additionally, GEO must include performance monitoring to ensure that content output remains aligned with your brand’s strategic goals.
As generative AI tools become more prominent in content creation and distribution, GEO is becoming essential for maintaining visibility and competitiveness in the digital space.
Why is GEO Important in 2025 and Beyond?
Generative engines like ChatGPT are rapidly growing in usage, fundamentally changing how people search for information and engage with content.
In 2024, ChatGPT alone surpassed Bing in visitor volume, receiving more than 10 million queries per day. And ChatGPT is just one of several platforms — others like Perplexity, Gemini, and CoPilot are also evolving, driving changes in the behavior of B2B buyers.
This shift means brands need to adapt to changing search behaviors. Generative AI is altering how audiences find and interact with information, and GEO ensures brands remain relevant in this evolving landscape.
Rather than replacing SEO, GEO complements it, allowing brands to achieve greater visibility across traditional search engines and AI platforms. We are currently seeing a growing intersection between organic search and generative AI, and several traditional SEO best practices do overlap with GEO to improve brand visibility.
Optimizing for generative models also has the potential to drive higher conversion rates. Early data suggests that AI-optimized content can perform better, and at Walker Sands, we leverage insights to further refine GEO strategies.
The bottom line? As generative engines continue to expand and evolve, GEO will be key for brands looking to maintain a competitive edge.
How do Generative Engines Work?
Generative engines like ChatGPT are Large Language Models (LLMs) with extensive neural networks that leverage a combination of pre-existing training data and continually updated information to generate responses to user prompts.
These LLMs are initially trained on extensive datasets, enabling them to understand language patterns, context, and a wide range of topics. To remain current, generative engines also tap into ongoing interactions, user feedback, new data inputs, and search engine results, allowing them to adapt to recent events, emerging trends, and fresh information.
For B2B brands, LLM adaptability is crucial for GEO because it allows generative engines to produce content that reflects the latest messaging, brand mentions, and shifts in industry dynamics.
By building a strong technical infrastructure, optimizing owned content for generative engines, and obtaining citations from AI-friendly outlets, brands can ensure their message is accurately and consistently represented in AI-generated outputs, enabling you to remain visible to your audience, maintain brand coherence, and capitalize on new trends in real-time.
What’s the Difference Between Generative Engine Optimization and SEO?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Search Engine Optimization (SEO) are both crucial strategies for enhancing a B2B brand’s visibility in the digital space, but they serve different purposes and focus on different aspects of content discovery.
Here’s a snapshot of Google search results, where we leveraged SEO best practices to improve visibility for a query:
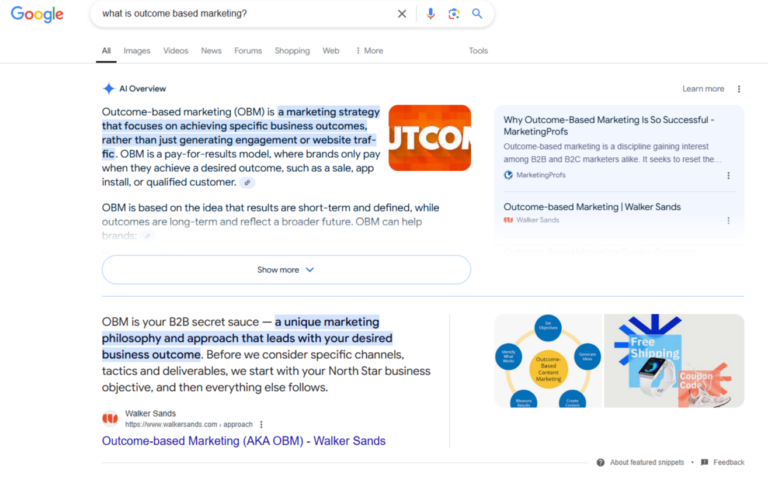
Here’s a snapshot response from Perplexity, using the same search query:
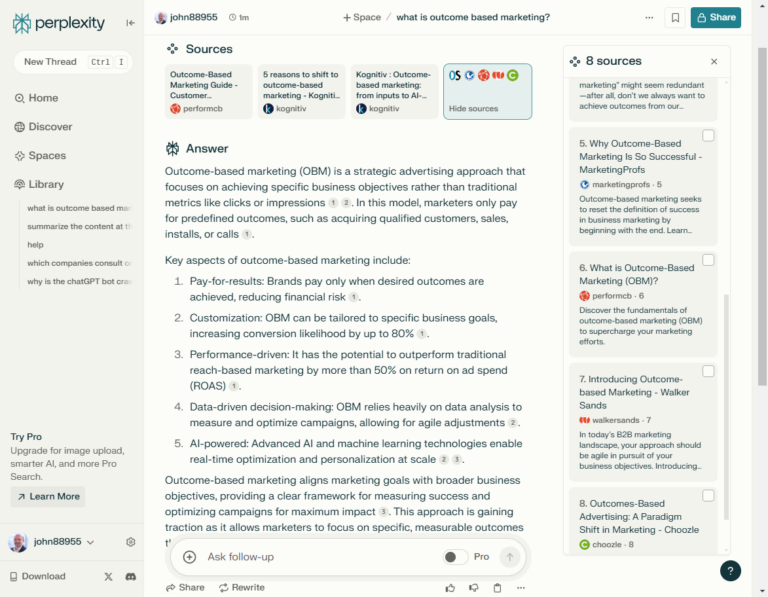
While SEO aims to optimize content for search engines like Google and Bing, GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI-driven generative models, such as ChatGPT and similar engines. Understanding both the similarities and differences helps brands leverage these tools effectively to stay competitive.
GEO and SEO Similarities
- Indexing: Search engines index content that is publicly available on the internet. LLMs build neural networks from information gathered from the internet, books, and other sources. AI systems and Search engines both leverage instructions provided by website owners to the bots that are looking for content or deciding if a brand’s content should be included in their index or model.
- Visibility: Both GEO and SEO are designed to improve visibility by understanding and catering to the behaviors of algorithms that rank and LLMs that generate responses.
- Optimization Elements: SEO relies on optimizing elements such as keywords, backlinks, page headings, and meta descriptions to increase keyword relevancy in order to rank content higher in search results. Similarly, GEO requires the optimization of various elements to provide context, including schema markups, headers, author assignments, the creation of author pages, and other strategies.
- Audience Targeting: Ultimately, both GEO and SEO are about delivering the right message to the right audience at the right time, ensuring brand visibility through search queries or AI-generated interactions.
GEO and SEO Differences
- Focus Areas: SEO is centered on making content indexable by search engines, while GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI systems that generate responses based on user prompts.
- Optimization Techniques: SEO involves optimizing factors like keywords, site structure, and backlinks to improve search rankings. GEO involves fine-tuning strategically selected text strings and providing additional context within website content that is consistent with and informed by brand messaging. This includes inline citations, concise introductions, added content depth, and more.
- Content Goal: SEO aims to bring users to your website through ranked search engine results in response to a user query. GEO, however, is more focused on ensuring that generative AI responses to user prompts accurately include and represent your brand, even if users do not end up visiting your site. GEO strives to have the brand’s owned and earned content cited by AI engines, along with a link to the cited content.
6 Key Ingredients of a Successful GEO Strategy
A successful GEO strategy involves multiple components to ensure effective optimization for AI-driven generative models.
- Research + Analysis: Research and analysis are essential for success. It’s important to identify relevant long-tail keywords, identify representative prompts and strategic phrases, analyze AI-generated responses to understand key terms, assess competitor strategies in generative engines, and evaluate how your site ranks in AI models to determine your share of voice.
- Content Strategy: A robust content strategy should leverage keyword and strategic research to create concise, keyword-rich content. Adding unique insights, incorporating multimedia, and keeping content updated helps maintain freshness. Assigning authors to content and creating author pages can add credibility, while concise introductions, authoritative links, schema markup, and effective header tags enhance search visibility and readability.
- Content Distribution: Content distribution involves sharing material in relevant online communities like Reddit and Quora, making use of user-generated content such as reviews or social posts, and building a community presence on social platforms like LinkedIn to expand reach and engagement.
- Brand Authority: Building brand authority requires maintaining consistency across all brand entities, developing an industry-focused backlinking strategy, and leveraging public relations efforts such as bylines, placements, influencer mentions, and press releases to enhance credibility and authority.
- Technical SEO/GEO: A sound technical website foundation is key to ensuring content accessibility. This includes optimizing page tags, improving page speed, and addressing crawl or indexing issues to make sure the right content is discoverable, usable, and includable in generative results.
- Measurement: Generative AI is currently not as measurable as mature channels like paid search, but tracking and measuring key aspects of Generative AI performance is still important. Your Analytics program can be configured to track Generative AI traffic and conversion performance from platforms such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, and others. Here is a snapshot of how measuring traffic from generative engines (via custom reporting) can look in Google Analytics 4:
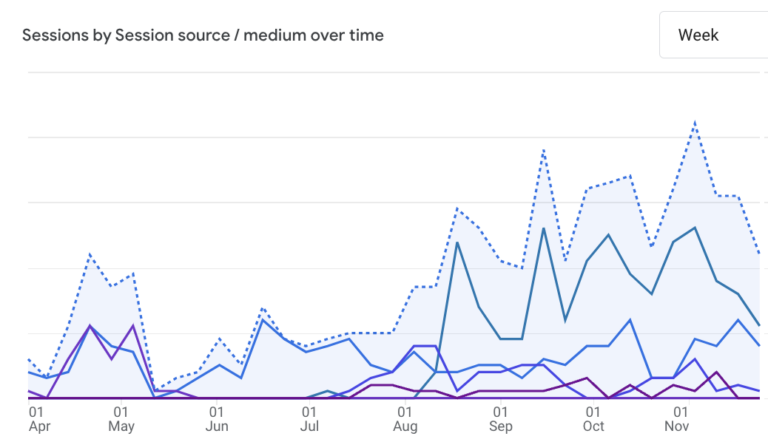
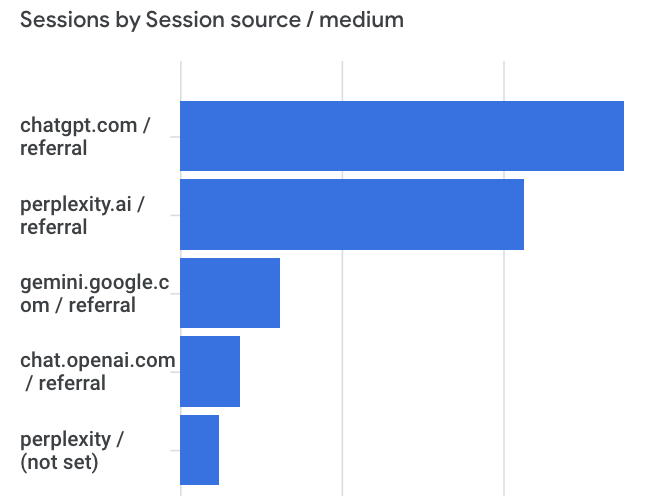
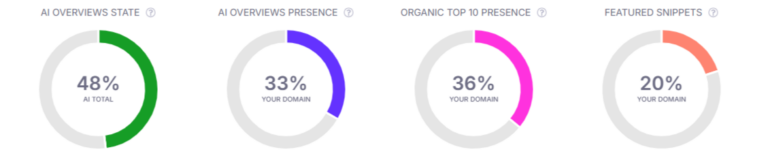
SEO rank-tracking tools are also beginning to include Google AI Overview display and citations:
Lastly, you should add Generative AI as a lead source in your CRM to track performance on opportunities and help measure your ROI.
Working with Walker Sands to Expand Your Generative Engine Footprint
Generative engine optimization (GEO) is rapidly becoming table stakes for B2B brands concerned about maintaining visibility in an AI-driven world. By optimizing content for generative models, you can ensure your brand remains relevant, accurate, and compelling across AI platforms.
GEO complements SEO, Content, and Public Relations, offering a comprehensive approach to digital visibility that is vital for success in 2025 and beyond.
Walker Sands has the expertise to help your brand thrive in the era of generative AI. Right out of the gate, we can assess your brand’s visibility across AI systems and provide a tailored roadmap for improving your GEO strategy. We can help you measure Generative AI performance on lead generation and pipeline to determine ROI.
If you’re ready to expand your reach and ensure your brand is visible and accurately represented in AI-generated content, contact us today to learn more about our services and how we can support your growth.
This is the second installment of our four-part blog series on AI in B2B marketing, check out the first piece on 10 Must-Attend AI Events for B2B Marketers in 2025 and stay tuned for more!
Ready to learn more about GEO and how it could enhance your marketing efforts? Reach out to our team today!


